WolfServe is our OpenSource drop in replacement for Apache2, you can create Apache2 configs, use certbot and utilities and it works fine. Supporting PHP it can get much faster responses.
It is fully OpenSource and you can get it from our GitHub
Contact Us for fast clustered Wolfserve/WolfProxy Hosting of your website or application.
A high-performance web server written in Rust that serves PHP applications via FastCGI with native SSL/TLS support and Apache configuration compatibility.
- Blazing Fast – Built on Axum & Tokio for maximum async performance
- PHP Support – Execute PHP files via FastCGI (php-fpm or php-cgi)
- SSL/TLS – Native HTTPS support with SNI for multiple domains
- Apache Compatible – Reads existing Apache vhost configurations
- Static Files – Serves static assets efficiently
- PHP FFI Bridge – Call Rust functions directly from PHP via libwolflib
- Admin Dashboard – Real-time monitoring, statistics, and request logging on port 5000
- Cross-Platform – Works on Debian/Ubuntu, Fedora/RHEL, Arch Linux, openSUSE
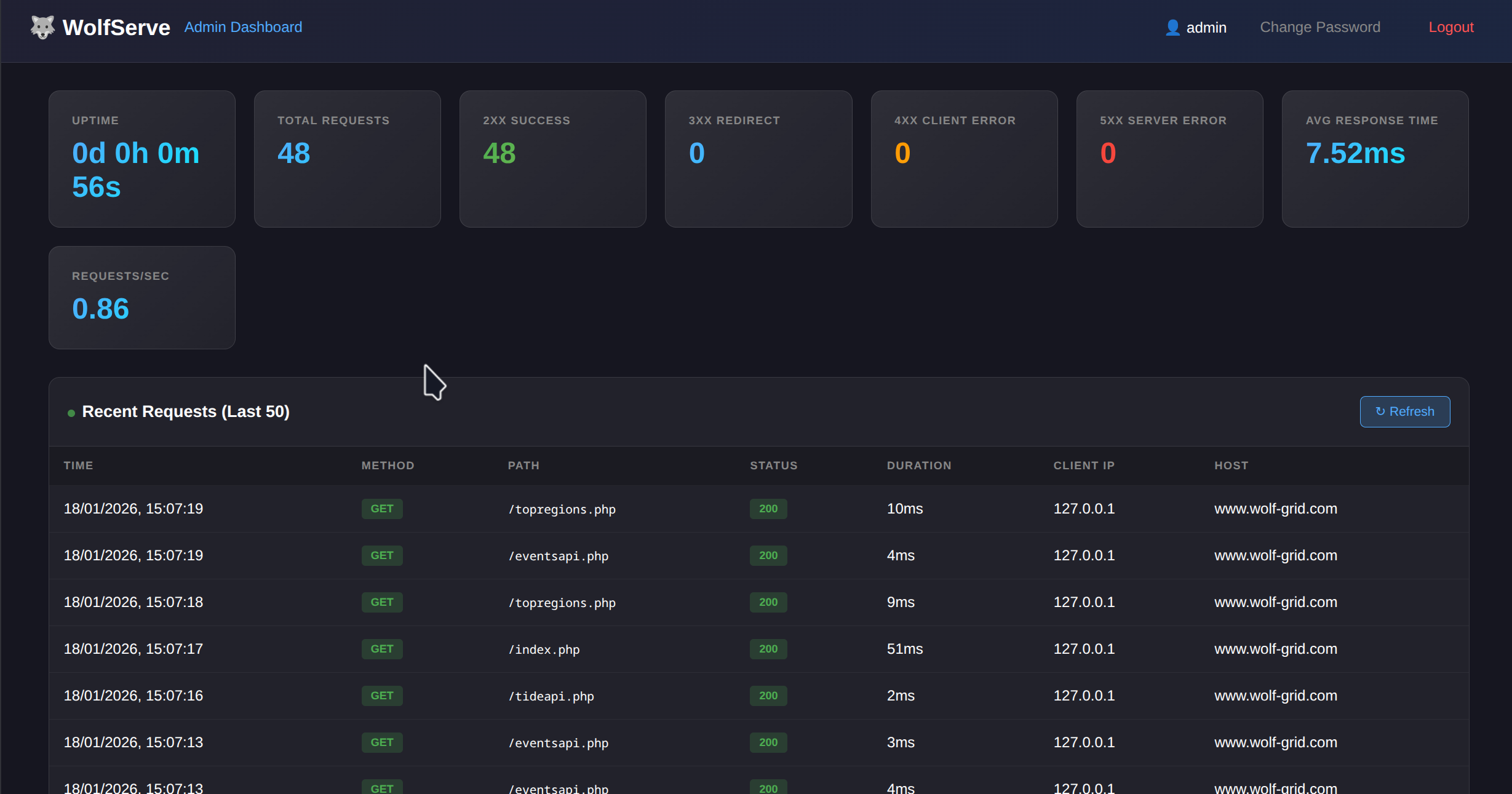
WolfServe includes a built-in admin dashboard accessible on port 5000 for monitoring and statistics.
- Real-time Statistics – Total requests, response codes (2xx/3xx/4xx/5xx), avg response time, requests/sec
- Request Logging – Last 50 requests with method, path, status, duration, client IP, and host
- Uptime Tracking – Server uptime displayed in days, hours, minutes, seconds
- Auto-refresh – Dashboard updates every 5 seconds
- Secure Authentication – Session-based login with bcrypt password hashing
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
⚠️ Important: Change the default password immediately after first login!
http://your-server:5000/
The dashboard binds to 0.0.0.0:5000 and is accessible from any interface, including through proxies.
Credentials are stored in wolfserve_admin.dat using base64 encoding with bcrypt password hashing. The file is created automatically on first run.
- Linux with systemd
- Rust 1.70+ (for building from source)
- PHP 7.4+ with php-fpm
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/wolfserve.git
cd wolfserve
# Run the installer (requires root)
sudo ./install.sh
# Start the server
./run.sh# Download the release package
tar -xzf wolfserve-x86_64-YYYYMMDD.tar.gz
cd wolfserve-x86_64-YYYYMMDD
# Run the installer (requires root)
sudo ./install_precompiled.sh# Build and install as systemd service
sudo ./install_service.sh
# The server will start automatically
systemctl status wolfserveEdit wolfserve.toml:
[server]
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 3000
[php]
fpm_address = "127.0.0.1:9993"
session_save_path = "/mnt/shared/wolfserve/sessions"
[apache]
# Load existing Apache vhost configs
# Debian/Ubuntu: "/etc/apache2"
# Fedora/RHEL: "/etc/httpd"
config_dir = "/etc/apache2"WolfServe supports shared PHP sessions across multiple servers, enabling seamless load balancing without sticky sessions.
Set session_save_path in wolfserve.toml to a shared network location:
[php]
fpm_address = "127.0.0.1:9993"
session_save_path = "/mnt/shared/wolfserve/sessions"- User logs in on Server A → session file created at
/mnt/shared/wolfserve/sessions/sess_abc123 - Next request routed to Server B → reads the same session file from shared storage
- User stays logged in seamlessly across all servers
- All servers must mount the same shared storage (NFS, GlusterFS, Ceph, etc.)
- Clocks should be synchronized (NTP) for consistent session expiry
- The installer automatically sets correct permissions (
chmod 1733with sticky bit)
The service installer prompts for all configuration options:
sudo ./install_service.sh
📝 Configuration Options (press Enter to accept defaults)
Server bind address [0.0.0.0]:
Server port [3000]:
PHP-FPM port [9993]:
PHP session save path [/var/lib/php/sessions]: /mnt/shared/wolfserve/sessions
Apache config directory [/etc/apache2]: Use environment variables for automated deployments:
sudo WOLFSERVE_SESSION_PATH="/mnt/shared/wolfserve/sessions" \
WOLFSERVE_PORT="3000" \
./install_service.sh -y| Environment Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
WOLFSERVE_HOST | Server bind address | 0.0.0.0 |
WOLFSERVE_PORT | Server port | 3000 |
WOLFSERVE_FPM_PORT | PHP-FPM port | 9993 |
WOLFSERVE_SESSION_PATH | PHP session save path | /var/lib/php/sessions |
WOLFSERVE_APACHE_DIR | Apache config directory | /etc/apache2 |
wolfserve/
├── src/
│ ├── main.rs # Main server code
│ ├── apache.rs # Apache config parser
│ └── admin.rs # Admin dashboard & authentication
├── wolflib/ # Rust library for PHP FFI
│ └── src/lib.rs
├── public/ # Web root directory
│ ├── index.php
│ └── rust.php # PHP FFI example
├── install.sh # Source installation script
├── install_service.sh # Systemd service installer
├── install_precompiled.sh # Precompiled binary installer
└── wolfserve.toml # Server configuration
WolfServe includes libwolflib.so, a Rust library that can be called directly from PHP using FFI:
<?php
$ffi = FFI::cdef("
int wolf_add(int a, int b);
char* wolf_greet(const char* name);
void wolf_free_string(char* s);
", "/opt/wolfserve/libwolflib.so");
// Call Rust from PHP!
$result = $ffi->wolf_add(10, 32); // Returns 42
$greeting = $ffi->wolf_greet("World");
echo FFI::string($greeting); // "Hello, World from Rust!"
$ffi->wolf_free_string($greeting);| Distribution | Package Manager | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu/Debian | apt | ✅ Fully Supported |
| Fedora | dnf | ✅ Fully Supported |
| RHEL/CentOS/Rocky | dnf | ✅ Fully Supported |
| Arch Linux | pacman | ✅ Supported |
| openSUSE | zypper | ✅ Supported |
# Start the service
sudo systemctl start wolfserve
# Stop the service
sudo systemctl stop wolfserve
# Restart the service
sudo systemctl restart wolfserve
# View logs
sudo journalctl -u wolfserve -f
# Check status
sudo systemctl status wolfserveApache Conflict: If Apache is running on ports 80/443, stop and disable it:
# Debian/Ubuntu sudo systemctl stop apache2 && sudo systemctl disable apache2 # Fedora/RHEL sudo systemctl stop httpd && sudo systemctl disable httpd
SELinux (Fedora/RHEL): The installer automatically configures SELinux permissions.
PHP Sessions: For single-server setups, sessions are stored in
/var/lib/php/sessions. For multi-server deployments, configuresession_save_pathto point to shared storage (see Multi-Server PHP Sessions).
# Build the server
cargo build --release
# Build the PHP FFI library
cd wolflib && cargo build --release
# Or use the build script
./build_lib.sh# Build and package for distribution
./package_release.sh
# Output: release-package/wolfserve-x86_64-YYYYMMDD.tar.gzContributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License – see the LICENSE file for details. You are free to use, modify, and distribute this software for both commercial and non-commercial purposes.


